Ex 1: For Positive Numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Python Program to calculate the square root
# Note: change this value for a different result
num = 8
# uncomment to take the input from the user
#num = float(input('Enter a number: '))
num_sqrt = num ** 0.5
print('The square root of %0.3f is %0.3f'%(num ,num_sqrt))
Output: The square root of 8.000 is 2.828
In this program, we store the number in num and find the square root using the ** exponent operator. This program works for all positive real numbers. But for negative or complex numbers, It will not work.
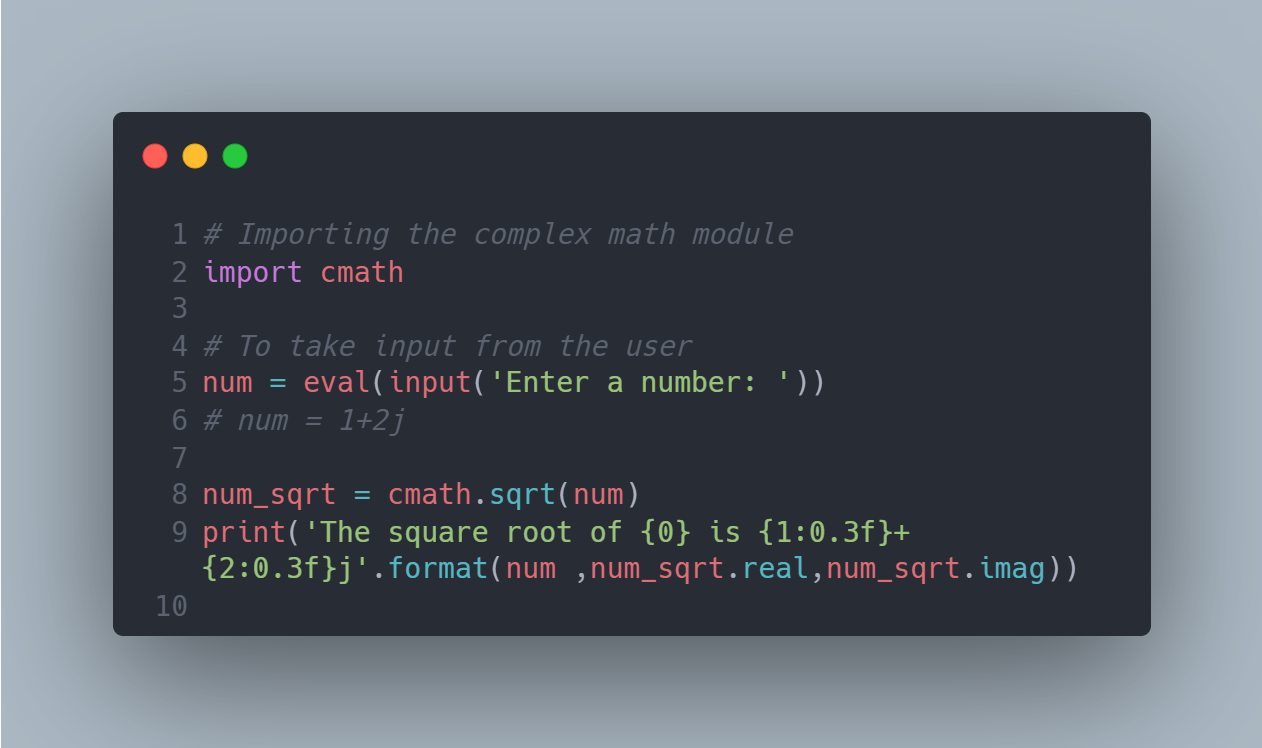
Ex 2: For Negative Numbers or Complex Numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Python Program to calculate the square root
import cmath
# Take input from the user
num = eval(input('Enter a number: '))
# num = 1 + 2j
num_sqrt = cmath.sqrt(num)
print('The square root of {0} is {1:0.3f}i + {2:0.3f}j'.format(num, num_sqrt.real, num_sqrt.imag))
Output:
Enter a number: -16
The square root of -16 is 0.000+4.000j
Enter a number: 16
The square root of 16 is 4.000+0.000j
The square root of (1+2j) is 1.272+0.786j
Enter a number: 3+4j
The square root of (3+4j) is 2.000+1.000j
In this program, we use the sqrt() function in the cmath (complex math) module.
Note: If we want to take complex number as input directly, like
3+4j, we have to use theeval()function instead offloat().
The
eval()method can be used to convert complex numbers as input to thecomplexobjects in Python. To learn more, visit Python eval() function.
Ex 3: Using F String
1
2
3
4
5
6
import cmath
num = 1 + 2j
num_sqrt = cmath.sqrt(num)
print(f'The square root of {num_sqrt} is {num_sqrt.real: 0.3f} + {num_sqrt.imag: 0.3f}j')
Output: The square root of (1.272019649514069+0.7861513777574233j) is 0.786+0.786j