Introduction to Python
- Python is an interpreted language. It means that Python directly executes the code line by line. It converts the source code that we write into an intermediate language, which is again translated into machine language that is executed.
What is Python?
- Python is a clear and powerful object-oriented programming language, comparable to Perl, Ruby, or Java.
- It is programming language that combines features of C and Java.
- Python is interpreted language1.
- Source code is stored in
.pyfile extension.
Note: In Java, if you want to make
hello worldprogram then you have to create whole class. But in C we can writeprintfin main function. In Python, we can write
History
- Python was created by Guido Van Rossum in 1990 at Stichting Mathematisch Centrum in the Netherlands as a successor of a language called ABC.
- Name
Pythonpicked from TV Show Monty Python’s Flying Circus of a BBC Comedy series.
- Timeline of Python:
Python 1 Python 2 Python 3 20 Feb 1991 16 Oct 2000 03 Dec 2008
Full Timeline of Versions
| Version | Launch Date |
|---|---|
| Python 0.9.0 | February, 1991 |
| Python 1.0 | January 1994 |
| Python 2.0 | October 2000 |
| Python 3.0 | December 2008 |
| Python 3.11 | October 2022 |
| Python 3.12 | October 2023 |
Python 3.5 + can not be used on Windows XP or earlier.
Features
- Easy to learn and use.
- High Level Language.
- Interpreted Language.
- It is Platform Independent.
- It is Procedure and Object Oriented both.
- It has huge library support.
- It is scalable
Applications
Major areas where Python is used are web application development, scientific and numeric computing, big data and machine learning.
Using Python we can make:
- Web Application - some framework like- Django, Flask, Pyramid, Bottle
- Desktop GUI Application - Tkinter, PyQt, PyGTK
- Console Based Application: Curses, Urwid, Urwid2
- Games and 3D Application: PyGame, Panda3D
- Mobile Application: Kivy
- Scientific and Numeric: SciPy, Pandas, IPython.
- Data Science: Pandas, NumPy, SciPy.
- Machine Learning - scikit-learn and TensorFlow
- Data Analysis - Matplotlib, Seaborn.
- Business Application: Odoo.
- Automation: Ansible, Salt, OpenStack.
Companies using Python
- Spotify
- Netflix
- Dropbox
- Quora
- Uber
- Mozilla
- Youtube
- Yahoo
- NASA
- IBM
- Nokia
How Python Works?
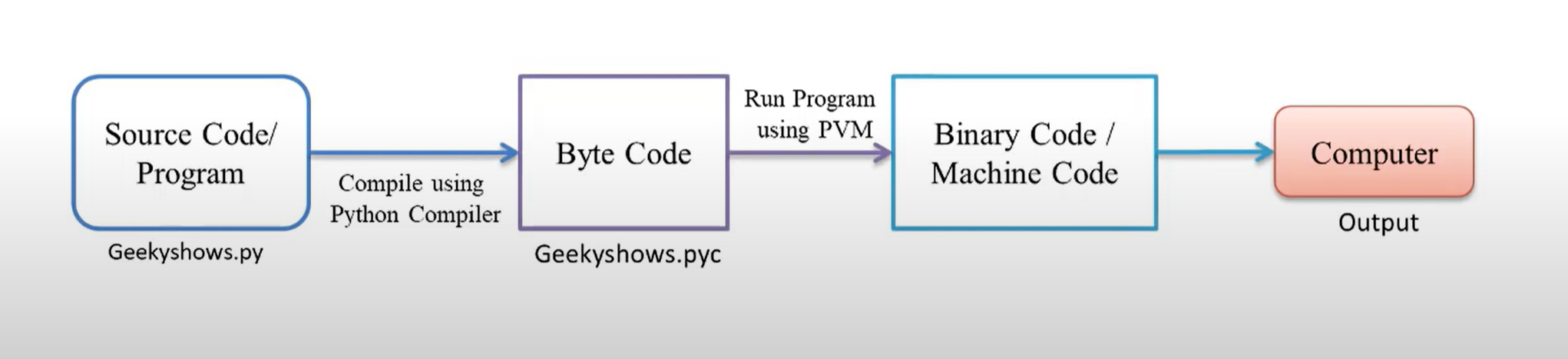
Python source code is compiled into byte code2, the internal representation of a Python program in the CPython interpreter. The byte code is also cached in .pyc files so that executing the same file is faster the second time (recompilation from source to byte code can be avoided). This “intermediate language” is said to run on a virtual machine that executes the machine code corresponding to each byte code. Do note that byte code is not expected to work between different Python virtual machines, nor to be stable between Python releases.
Python Compiler: A Python Compiler converts the program source code into byte code.
Type of Python Compilers
- It is also known as implementation of Python, interpreter or flavours of Python. There are 4 types of Python Compilers:
- CPython: Standard Python compiler made in C Language. It is used for general purpose.
- Jython / JPython: It is made in Java Language. It is used for Java Applications.
- IronPython: It is made in C# Language. It is used for .NET Framework.
- PyPy: It is made in Python Language. It is used for speed up the execution of Python code.
Other Python Compilers:
- RubyPython: It is made in Ruby Language.
- StacklessPython: It is made in C Language. It is used for Multi-threading.
- Pythonxy: It is made in C Language. It is used for Data Science.
- AnacondaPython: It is made in C Language. It is used for Data Science.
Working of Python -
- Write your Source Code / Program (.py extension).
- Compile the program using Python Compiler.
- Compiler Converts the Python Program into byte Code (.pyc extension).
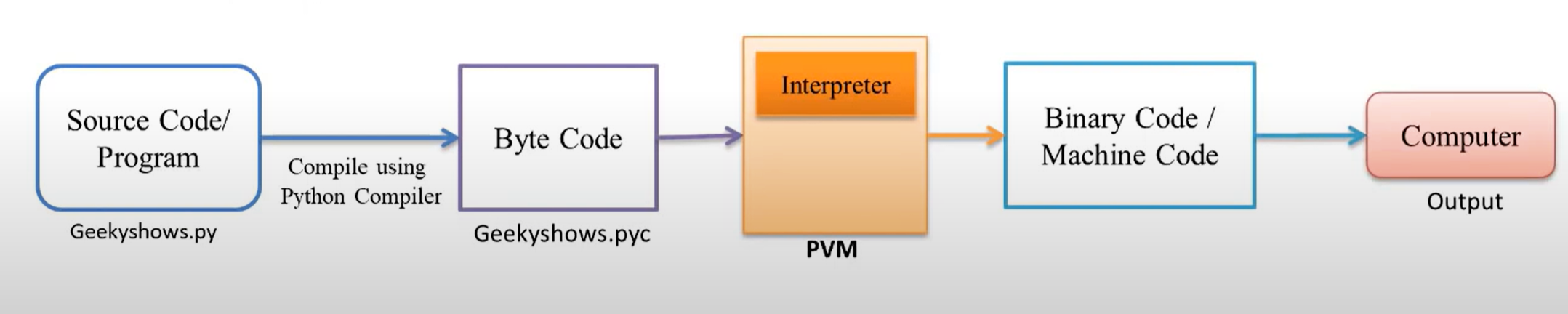
- Computer/ Machine can not understand Byte Code so we convert it into Machine Code using PVM3 (Python Virtual Machine).
- PVM3 uses an interpreter which understands the byte code and convert it into machine code.
- Machine Code instructions are then executed by the processor and results are displayed.
Installation
You have to download two things -
- Install Python: 👉🏻 Download Python
- Install IDE4: 👉🏻Download VS Code Editor
Note: Make sure check the box of
Add Python 3.9 to PATHwhile installing python. It will add python to your system environment variable. otherwise will get error while running python in terminal.
Commands
- Check Python Version:
1
python --version- Run Python File:
1
python filename.py
- Install External Module:
1
pip install module_name
REPL:
REPL stands for Run Evaluate Print Loop by writing python.
Start REPL: :
1
2
# write python in terminal to open REPL
python
Run Python using command line: :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# importing built-in modules gives no error
import random
import math
# External module need to be install
import flask
import pandas
# Getting Error: (Not Found)
Addition, Multiplication, Expression, True Division, Integer Division: :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Addition
>>> 20 + 56 + 25
# Multiplication
>>> 56 * 10
# Expression
>>> 10 * 4 + 3 * 4 + 34 * 2
# True Division
>>> 32 / 8 # Float value
# Integer Division
>>> 32 // 8 # Int value
Exit REPL: :
1
2
# To exit the terminal
exit()
Note:
pipstands for Preferred Installer Program. It is a command-line utility that acts as package manager for python to install, reinstall or uninstall PyPi packages.
Some Tips:
- Don’t use module name as “Python file” name like flask, pandas etc.
- You can use multiple interpreter like python 3.9, 3.8, 3.7 e.t. simultaneously in Pycharm
- Module:
- Built in Module - already in python
- External Module - download from internet
Explanation
An interpreter is a computer program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been compiled into a machine language program. Statements ae executed line by line. An interpreter generally uses one of the following strategies for program execution: parse the source code and perform its behavior directly; translate source code into some efficient intermediate representation and immediately execute this; explicitly execute stored precompiled code made by a compiler which is part of the interpreter system. ↩
Byte code represents the fixed set of instructions created by python developers representing all type of operations like (arithmetic operation, comparison operation, memory related operation etc). The size of each byte code instruction in 1 byte or 8 bits. We can find byte code instruction in the
.pycfile. ↩Python Virtual Machine (PVM) is a program which provides programming environment. The role of PVM is to convert the byte code instructions into machine code so the computer can execute those machine code instruction and display the output.
![PVM]() ↩ ↩2
↩ ↩2IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment. It is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not. The boundary between an integrated development environment and other parts of the broader software development environment is not well-defined. Sometimes a version control system, or various tools to simplify the construction of a graphical user interface (GUI), are integrated. Many modern IDEs also have a class browser, an object browser, and a class hierarchy diagram, for use in object-oriented software development. ↩